|
_small.png)
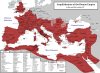
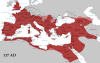
The Roman Empire
was the post-Republican period of ancient Rome. As a polity it
included large territorial holdings around the Mediterranean Sea
in Europe, Northern Africa, and Western Asia ruled by emperors.
From the accession of Caesar Augustus to the military anarchy of
the 3rd century, it was a principate with Italy as metropole of
the provinces and the city of Rome as sole capital (27 BC AD
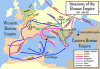
286). After the military crisis, the empire was ruled by
multiple emperors who shared rule over the Western Roman Empire
and over the Eastern Roman Empire. Rome remained the nominal
capital of both parts until AD 476, when the imperial insignia
were sent to Constantinople, following the capture of Ravenna by
the barbarians of Odoacer and the subsequent deposition of
Romulus Augustulus. The adoption of Christianity as the state
church of the Roman Empire in AD 380 and the fall of the Western
Roman Empire to Germanic kings conventionally marks the end of
Classical antiquity and the beginning of the Middle Ages.
Because of those events, along with the gradual hellenization of
the Eastern Roman Empire, historians distinguish the medieval
Roman Empire that remained in the Eastern provinces as the
Byzantine Empire.
The predecessor state of the Roman Empire, the Roman Republic
(which had replaced Rome's monarchy in the 6th century BC)
became severely destabilized in a series of civil wars and
political conflicts. In the mid-1st century BC, Julius Caesar
was appointed as perpetual dictator and then assassinated in 44
BC. Civil wars and proscriptions continued, eventually
culminating in the victory of Octavian, Caesar's adopted son,
over Mark Antony and Cleopatra at the Battle of Actium in 31 BC.
The following year Octavian conquered Ptolemaic Egypt, ending
the Hellenistic period that had begun with the conquests of
Alexander the Great of Macedon in the 4th century BC. Octavian's
power then became unassailable, and in 27 BC the Roman Senate
formally granted him overarching power and the new title
Augustus, effectively making him the first Roman emperor.
The first two centuries of the Empire saw a period of
unprecedented stability and prosperity known as the Pax Romana
("Roman Peace"). Rome reached its greatest territorial expanse
during the reign of Trajan (AD 98117). A period of increasing
trouble and decline began with the reign of Commodus (177192).
In the 3rd century the Empire underwent a crisis that threatened
its existence, as the Gallic Empire and Palmyrene Empire broke
away from the Roman state, and a series of short-lived emperors,
often from the legions, led the empire. The empire was reunified
under Aurelian (r. 270275). In an effort to stabilize it,
Diocletian set up two different imperial courts in the Greek
East and Latin West in 286. Christians rose to positions of
power in the 4th century following the Edict of Milan of 313.
Shortly after, the Migration Period, involving large invasions
by Germanic peoples and by the Huns of Attila, led to the
decline of the Western Roman Empire. With the fall of Ravenna to
the Germanic Herulians and the deposition of Romulus Augustus in
AD 476 by Odoacer, the Western Roman Empire finally collapsed;
the Eastern Roman Emperor Zeno formally abolished it in AD 480.
On the other hand, the Eastern Roman Empire survived for another
millennium, until Constantinople fell to the Ottoman Turks of
Sultan Mehmed II in 1453.
Due to the Roman Empire's vast extent and long endurance, the
institutions and culture of Rome had a profound and lasting
influence on the development of language, religion, art,
architecture, literature, philosophy, law, and forms of
government in the territory it governed, and far beyond. The
Latin language of the Romans evolved into the Romance languages
of the medieval and modern world, while Medieval Greek became
the language of the Eastern Roman Empire. The Empire's adoption
of Christianity led to the formation of medieval Christendom.
Greek and Roman art had a profound impact on the Italian
Renaissance. Rome's architectural tradition served as the basis
for Romanesque, Renaissance and Neoclassical architecture, and
also had a strong influence on Islamic architecture. The
rediscovery of Greek and Roman science and technology in
Medieval Europe led to the Scientific Renaissance and Scientific
Revolution. The corpus of Roman law has its descendants in many
legal systems of the world today, such as the Napoleonic Code,
while Rome's republican institutions have left an enduring
legacy, influencing the Italian city-state republics of the
medieval period, as well as the early United States and other
modern democratic republics. |
About TransAnatolie
Tour (Multi-Lingual Cultural Tour Operator)
TransAnatolie Tour is a subgroup of Anadolu
and is a Multi-Lingual Cultural Tour Operator in Anatolia (Asia
Minor) Turkey.TransAnatolie Tour
has the ambition and the capacity to be become one of the leading provider and
operator of archaeological, historical, belief (biblical) and cultural
heritage tours and specialty travel with high Quality of Service (QoS)
concept.
TransAnatolie Tour develops its programs with a network of
Specialists, who are well recognized, local, regional, national, and international
professionals at the top of their fields. These Specialists share their
knowledge, insights and vision providing an in-depth insiders understanding of
what distinguishes a particular culture and what factors shaped its evolution.
TransAnatolie Tours are executed in five
languages (Dutch, English, French, German and Turkish) with high QoS concept
by Tourism Professionals of valuable experience, intelligence and high
intellectual capacity.
TransAnatolie Tour executive and operations
teams have been at the cutting edge of international tour (holiday) operations
and specialty travel since 1990s, working with organizations, universities and
museums to provide unique travel experiences, cultural and belief (biblical) tours
(holidays/trips) to their memberships.
Multi-Lingual TransAnatolie Tour team members
have many years of valuable experience in providing individuals and
organizations with high quality cultural, historical, belief/biblical,
archaeological, architectural tours and travel experiences with high quality of
service (QoS).
TransAnatolie has immersed travelers in
Anatolia's most fascinating ancient cultures and provided enriching travel
experiences.
TransAnatolie (International Multi-Lingual
Cultural Tour Operator) has also been in small boat cruises, building exciting
travel packages around these unique vessels.
TransAnatolie is now
expanding its distribution by making these high quality, unique travel
products and programs available to the public. Supported by our international
network of offices and affiliates worldwide, the aim of TransAnatolie Team of
travel professionals and passionate program specialists is to make your next
'vacation' a truly rewarding travel experience.
TransAnatolie Tour is a member of
-
Turkish Ministry of Culture and Tourism (Licence
No. 4938),
-
Ankara Chamber of Commerce (Trade registry under
No. 54/1024),
-
Turkish-French Cultural Association,
-
Turkish Association at the United Nations,
-
Union of Turkish Tour Operators (TÜRSAB),
-
Union of Multi-Lingual Professional Tourism Guides (TUREB-ARED),
-
Ankara Cultural Tourism Association (BATUDER),
-
Nigde Cultural Association,
-
Aksaray Cultural Association,
-
Arts & Cultural Association of Taspinar.
-
TransAnatolie Tour
- A - Group
License N°4938 - The Turkish Ministry of Culture and Tourism
|




_small.png)